In today’s digital era, cloud computing has become an indispensable part of the technological landscape, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and individuals access services. From storing vast amounts of data to deploying complex applications, cloud computing offers unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. In this article, we’ll delve into key aspects of cloud computing, including big data, deployment steps, the role of AWS, and crucial security considerations.
Understanding Big Data in Cloud Computing
Big data refers to the massive volume of structured and unstructured data that inundates businesses on a daily basis. This data comes from various sources, including social media, sensors, devices, and enterprise applications. In the context of cloud computing, big data analytics involves processing and analyzing these vast datasets to uncover valuable insights and patterns that can drive informed decision-making.
Cloud computing provides the ideal infrastructure for big data analytics due to its ability to store and process large volumes of data efficiently. By leveraging cloud-based platforms and services, organizations can scale their analytics workloads dynamically, without the need for substantial upfront investments in hardware or infrastructure.
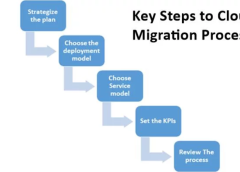
The Primary Steps in Deploying a Cloud Computing Offering
Deploying a cloud computing offering involves several key steps to ensure a smooth and successful implementation. The primary steps include:
- Assessment and Planning: Begin by assessing your organization’s current IT infrastructure, requirements, and objectives. Identify workloads that are suitable for migration to the cloud and develop a comprehensive migration strategy.
- Provider Selection: Choose a cloud service provider that aligns with your business needs, budget, and compliance requirements. Consider factors such as service offerings, pricing models, security features, and geographic availability.
- Migration and Deployment: Execute the migration of workloads to the cloud according to the defined strategy. This may involve rehosting, refactoring, or rearchitecting applications to optimize performance and scalability in the cloud environment.
- Integration and Optimization: Integrate cloud services with existing systems and applications, ensuring seamless connectivity and interoperability. Continuously monitor and optimize performance, resource utilization, and costs to maximize the value of your cloud investment.
The Role of AWS in Cloud Computing
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading cloud service provider, offering a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services that empower organizations to build, deploy, and manage a wide range of applications and workloads. With a vast global infrastructure comprising data centers in multiple regions, AWS provides high availability, reliability, and scalability for businesses of all sizes.
AWS offers a diverse portfolio of services, including compute, storage, databases, networking, machine learning, and analytics. From hosting websites and mobile apps to running enterprise workloads and performing data analytics, AWS provides the building blocks and tools necessary to drive innovation and accelerate digital transformation.
Security Risks in Cloud Computing
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, it also introduces unique security risks and challenges that organizations must address proactively. Some common security risks in cloud computing include:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data stored in the cloud can result in data breaches, leading to financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
- Identity and Access Management: Poorly managed user identities and access controls can expose cloud resources to unauthorized users, increasing the risk of data breaches and insider threats.
- Compliance and Governance: Compliance with industry regulations and data protection laws is crucial in the cloud environment. Failure to comply with regulatory requirements can result in legal consequences and financial penalties.
- Data Loss and Service Disruptions: Data loss due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or malicious attacks can disrupt business operations and lead to data recovery challenges in the cloud.
To mitigate these security risks, organizations should implement robust security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, network segmentation, regular audits, and security monitoring. Additionally, partnering with a reputable cloud service provider that prioritizes security and compliance can help organizations enhance their overall security posture in the cloud.
Maximizing the Benefits of Cloud Computing
Beyond addressing security risks, organizations can unlock additional benefits by maximizing their utilization of cloud computing resources. Here are some strategies to enhance the value derived from cloud investments:
- Cost Optimization: Cloud computing offers cost advantages through pay-as-you-go pricing models and the ability to scale resources based on demand. By optimizing resource utilization, rightsizing instances, and leveraging cost management tools provided by cloud providers, organizations can optimize their cloud spending and reduce overall costs.
- Innovation and Agility: Cloud computing fosters innovation by providing access to cutting-edge technologies and services, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT). By leveraging these technologies, organizations can accelerate innovation, streamline business processes, and gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing enables organizations to scale their infrastructure and applications dynamically to accommodate changing business needs and fluctuating workloads. Whether experiencing sudden spikes in traffic or launching new products/services, the elasticity of the cloud allows organizations to scale up or down seamlessly without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware or infrastructure.
- Global Reach and Accessibility: Cloud computing eliminates geographical barriers and enables organizations to reach global audiences with ease. With data centers located in multiple regions worldwide, cloud providers offer low-latency access to services and ensure high availability and reliability for users across the globe.
- Focus on Core Competencies: By offloading infrastructure management and maintenance tasks to cloud providers, organizations can focus more resources and energy on core business activities and strategic initiatives. Cloud computing allows businesses to delegate routine tasks, such as provisioning servers, managing storage, and maintaining security, to experienced cloud professionals, freeing up internal teams to innovate and drive growth.
In essence, cloud computing empowers organizations to accelerate digital transformation, drive innovation, and achieve greater agility and efficiency in today’s fast-paced business landscape. By embracing cloud technologies strategically and implementing best practices, organizations can maximize the benefits of cloud computing and position themselves for long-term success.